Chest Xray (Each Oblique View) Orbit XMastoids XRay may be performed to assess damage to the ear as well as the source of pain and discomfort to the area There are multiple XRay views when checking your mastoids Who should get this test?View and Download PowerPoint Presentations on X Ray Mastoid PPT Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPointcom, find free presentations research about X Ray Mastoid PPT
Neuroradiology Back To The Future Head And Neck Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology
How to do mastoid x ray
How to do mastoid x ray-Mastoid Xray (Laws & Mayers) Chest Bucky (Ap) Mastoiditis; Investigations Examination under microscope C/S from discharge Rigid oto endoscopy – to see facial recess and sinus tympani if possible PTA Xray mastoid schuller's & laws view HRCT temporal bone 17




Skull Series Occipitofrontal Projection 0 Cr Clinical Indications
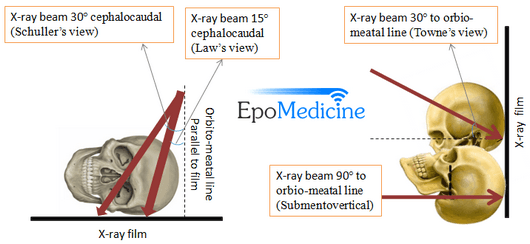
Axiolateral ObliqueModified Law Method CENTRAL RAY CR directed to a midpoint of the grid at an angle of 15 degrees caudad to exit the downside mastoid tip approximately 1 inch posterior to the EAM The CR enters approximately 2 inches posterior to, and 2 inches superior to the uppermost EAMChest Xray (Apicolordotic View) Neck Xray;Laws view mastoids positioning" Keyword Found Websites Keywordsuggesttoolcom DA 28 PA 39 MOZ Rank 69 Schuller's view is a lateral radiographic view of skull principally used for viewing mastoid cellsThe central beam of Xrays passes from one side of the head and is at angle of 25° caudad to radiographic plate
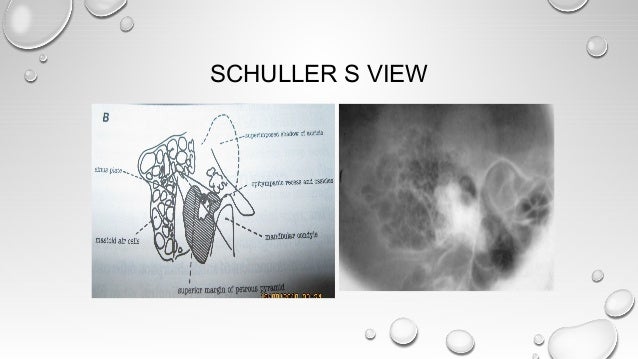
A plain Xray of mastoid/Law's view was done to assess the position of dural and sinus plates Routine haematological and biochemistry investigations were done to assess fitness for anaesthesia After the examination and appropriate investigations informed consent was taken for participation in the trialSchüller's view (Runstrom) is a lateral view of the mastoid obtained with the sagittal plane of the skull parallel to the film and with a 30° cephalocaudal angulation of the xray beam These 30° in Schüller's view displaces the arcuate eminence of the petrous bone downward and shows the antrum and the upper part of the attic Xray signs of acute mastoiditis are the decrease or absence of airiness of the cells of the mastoid process and violation of the integrity of the bone septa separating them The formation of destructive foci With chronic otitis, the cells are darkened, thinning occurs, and sometimes the septa between them are destroyed
Central Ray The horizontal central ray is centered in the midline of the occiput so that the emergent ray exits the patient in the midline at the level of the anterior nasal spine at the upper border of the maxilla Various views for mastoid • LAW's view lateral Oblique view Usually these projection taken in open and closed mouth positions Modified Law method is an xray special projection to best demonstrate the abnormal relationship of temporomandibular fossa or TMJ, which also known as rang of motion between condyles and TM fossa Commonly this projectjion is taken in open and closed mouth positionThe Xray mastoid is done to know mastoid pneumatisation and the level of sinus and dural plates Xray mastoids were obtained by Law's view bilaterally and high resolution computed tomography of the temporal bone was obtained with 1mm cuts in axial and coronal planes
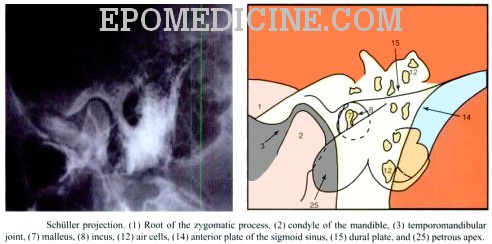



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255
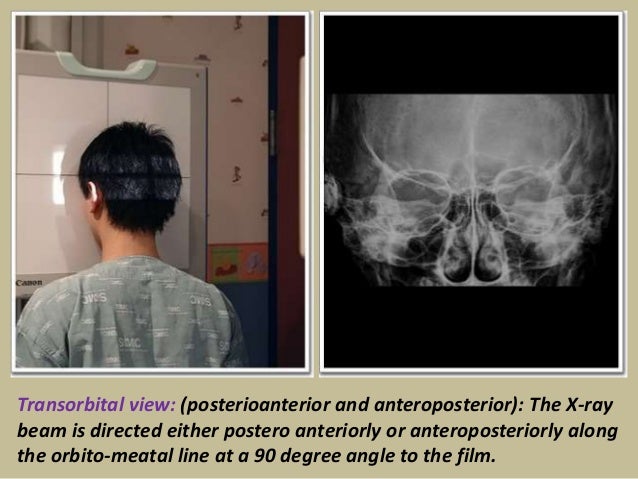
Abstract DURING the past 17 years, I have treated 41 cases of mastoiditis with Xrays Of these, 16 acute cases were seen in children Of the adults, 15 were acute, seven subacute, and three chronic The chief complaints in all were pain, tenderness to pressure over the mastoidThe Xray beam is directed either postero anteriorly or antero posteriorly along the orbitomeatal line at an angle of 90 degrees to the film Price for XRay Mastoid (Right) (AP View) Test Average price range of the test is between Rs300 to Rs500 depending on the factors of Mastoid process (Processus mastoideus) The skull is composed of multiple small bones held together by fibrous joints Its inferior surface gives rise to a number of projections, and these allow for the attachment of many structures of the neck and faceThe temporal bone is one of the bones of the skull
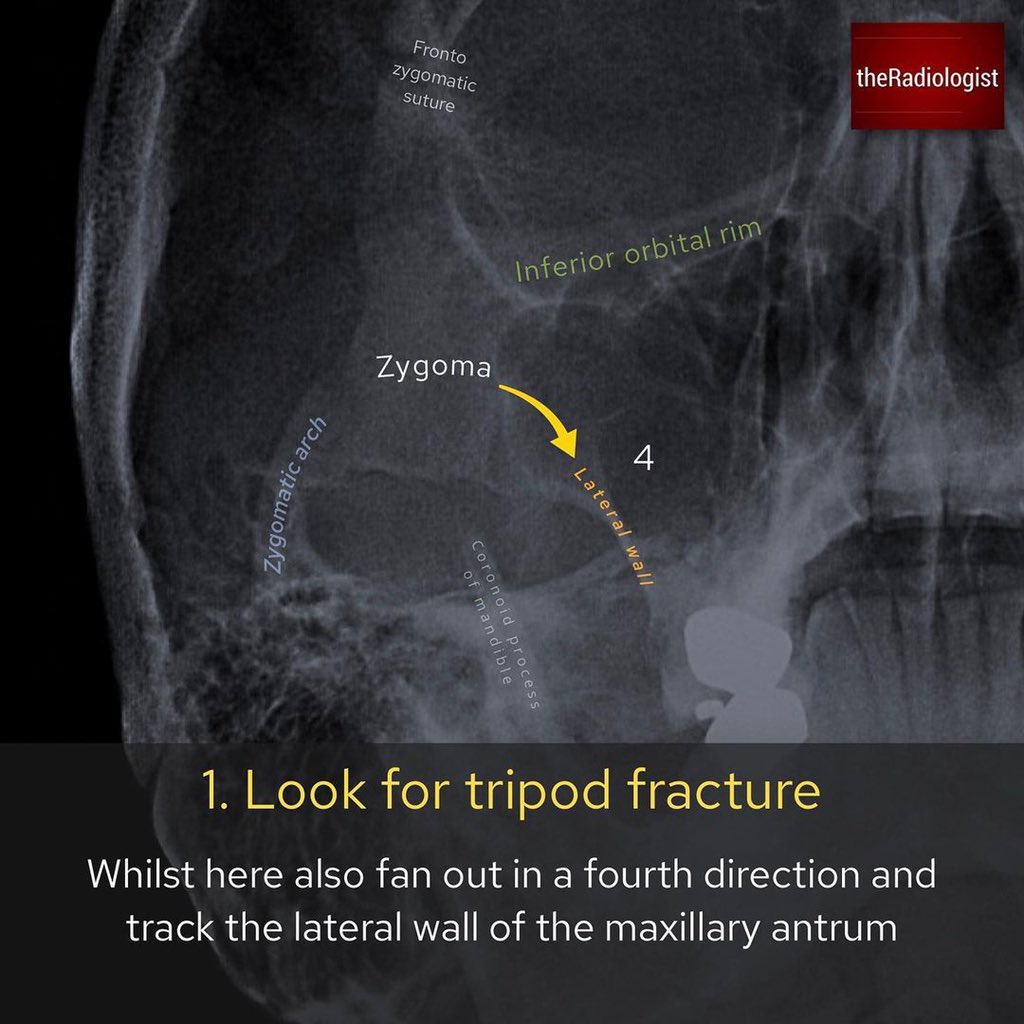



Mohammed Mahri محمد مهري Occipito Mental Radiograph Of The Facial Bones The Facial Bone X Ray Is Being Replaced With Ct In Many Places But In Some Places Around The




X Rays In Ent
Lateral oblique view / Mastoid Sculler's view Clinical indication Fracture, mastoiditis, tumor Region Mastoid process, mastoid air cells Patient's Position Ask the patient to lie in prone position Central ray The central ray is directed at an angle of 30° towards the feet The central ray enters the skull above the ear atNasal Bone – apl (Water's View And Soft Tissue Lat) Chest Xray (Ap, Lat Below 5 Yrs Old) Nasal Bone Soft Tissue Lat;XRay imaging for MASTOID Performed on a Digital XRay Please note that these scans involve XRay radiation, and are not to be performed during pregnancy Test Type Radiology Preparation No Special Preparation Required Reporting Within 24 Hours* Test Price Please choose Location and other options on this page to view final cost in Delhi NCR




Right Well Developed Aerated Mastoid Lateral X Ray Download Scientific Diagram
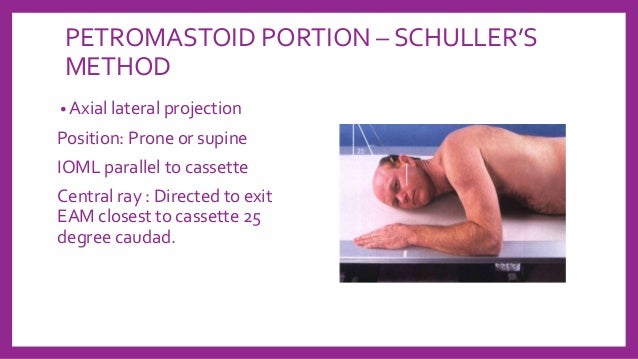



Skull Radiography Techniques And Reporting
Posteromarginal Perforation with Polyp in Cholesteatoma A similar lesion involving the right ear The patient presented with scanty foulsmell ear discharge, dizziness, reduced hearing and headache The eardrum appeared severely retracted with granulation seen at the periphery posteriorly and yellow pus in proximityInfant skull xray lateral view this is an xray image of the skull of an infant taken from a lateral view showing the skull from the side showing 1 frontal bone 2 parietal bones 3 occipital bone 4 lambdoid suture 5 ocular sockets 6 vertex 7 temporal bone 8 mastoid air cells 9 the manXray mastoids were obtained by Law's view bilaterally and high resolution computed tomography of the temporal bone was obtained with 1mm cuts in axial and coronal planes Purpose of the study to compare regarding the pneumatisation in chronic suppurative otitis media with xray both mastoids and HRCT temporal bone




Combined Radiographic And Anthropological Approaches To Victim Identification Of Partially Decomposed Or Skeletal Remains Radiography



Nanopdf Com Download File 3159 Pdf
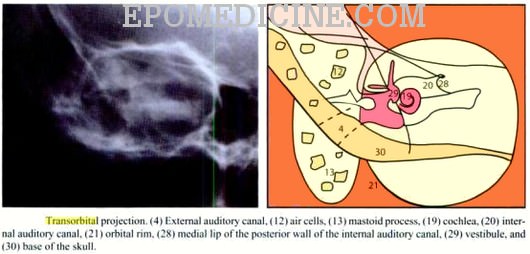
Before thinsection highresolution CT, many Xray views and modifications were used Today, only few views are used STENVERS VIEW – oblique projection (angled 45° forward) to provide unobstructed view of petrous bone, bony labyrinth, internal auditory canal SCHÜLLER VIEW – along ear canal – demonstrates mastoid air cellsThe xray study of the mastoid region, which was begun in March, 1908, has undergone a slow but gratifying metamorphosisUndertaken with grave doubts as its practical value, it has developed into a method which rivals in its accuracy other recognized methods of physical examinationVIEWS LAW MAYER STENVER TOWNE First major axiscomponent or analyte Property FIND Second major axisproperty observed (eg, mass vs substance) Time Aspect PT Third major axistiming of the measurement (eg, point in time vs 24 hours) System HEAD>MASTOIDBILATERAL




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



1
Mastoids XRay is usually ordered by doctors if you have these indications Fever, irritability, and lethargy Sclerosed mastoid and cavity on xray mastoids and HRCT temporal bone as shown in fig 2 and fig 3 respectively In normal ears, the coincidence of xray and HRCT findings of status of mastoid was 972% except in one case (28%) there was a difference as shown in table 4 In this case it was sclerotic on xray but diploeic on HRCT Lateral, oblique, anteroposterior, and semiaxial views and modifications of these views were produced by angulation of the xray beam or the patient's head The lateral mastoid view ( Fig 381 ) is the only projection still used in some imaging centers, largely to confirm a diagnosis of acute mastoiditis or substantiate previous mastoid disease




How To Do Mastoids In X Ray Table Youtube




The Modified Stenver S View For Cochlear Implants What Do The Surgeons Want To Know
Laws view mastoids positioning" Keyword Found Websites Keywordsuggesttoolcom DA 28 PA 39 MOZ Rank 69 Schuller's view is a lateral radiographic view of skull principally used for viewing mastoid cellsThe central beam of Xrays passes from one side of the head and is at angle of 25° caudad to radiographic plateVersion 269 XR Mastoid bilateral Law and Mayer and Stenver and TowneActive FullySpecified Name Component Views Law Mayer Stenver Towne Property Find Time Pt System Head>Mastoidbilateral Scale Doc Method XR Additional Names Short Name XR MastoidBl LawMayerStenverTowne Associated Observations This panel contains the recommendedRoutinely xray mastoids are advised as a preoperative imaging modality A comparative study of plain xray mastoids with HRCT temporal bone in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media Xray mastoids Schuller's view (right and left) was done and the radiological features were noted




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
6 An xray mastoids lateral oblique view (Laws) showed (L) mastoid to be sclerotic with evidence of bone destruction 6 Sethi et al evaluated the influence of presence and duration of chronicCT has typically overtaken xray as the modality of choice for imaging of the mastoid This is a normal mastoid series for reference 1 article features images from this caseIn a good quality xray, it avoids overlap of impressions of both mastoid bones during imaging, separate xrays of both mastoid bones is taken it is an alternative x ray to the Law projection where 15 degrees is used



Http Www Angelfire Com Sk3 Kshemaent Students Ent Radiology A Pdf



Mastoids Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
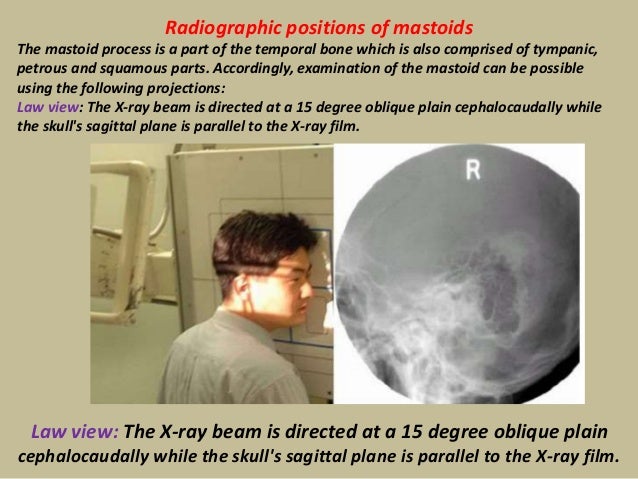
Infant skull xray lateral view this is an xray image of the skull of an infant taken from a lateral view showing the skull from the side showing 1 frontal bone 2 parietal bones 3 occipital bone 4 lambdoid suture 5 ocular sockets 6 vertex 7 temporal bone 8 mastoid air cells 9 the man If the patient is positioned in such a way that the lens is outside the direct xray beam, the dose is in the order of 0003 Gy 5 Although the typical dose to the lens from a single CT scan is much lower than the threshold value for a cataract, multiple nonoptimized scans in a short time with the lens in the xray beam can result in a lens Accordingly, examination of the mastoid can be possible using the following projections Law view The Xray beam is directed at a 15 degree oblique plain cephalocaudally while the skull's sagittal plane is parallel to the Xray film Law view The Xray beam is directed at a 15 degree oblique plain cephalocaudally while the skull's sagittal plane is parallel to the Xray film



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




60 Radiographs Labeling Ideas Radiography Radiology Technologist Radiology
Write down the differential diagnosis Xray both mastoids Laws view (lateral oblique) Differential diagnosis 1 Large antral cell This is usually bilateral 2 Cholesteatomatous cavity Radiologically this cavity will be surrounded by a rim of sclerosis 3 Operated cavity Pt will give h/o mastoidPressure worried about mastoiditis no redness around ear no fever My infected tooth doesn t hurt any more bu do have positional dizziness couldn t go toThe classic radiographic assessment of mastoid air cell system size is the Runström II view, but the Law lateral view is the commonly used clinical view in the United States Isolated temporal bone specimens are most accurately positioned using a modified Law Lateral view (with the film perpendicular to the central Xray beam)



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
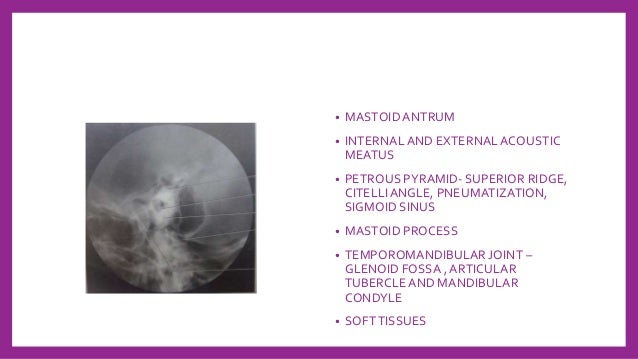



Skull Radiography Techniques And Reporting
The central beam of Xrays passes from one side of the head and is at angle of 25° caudad to radiographic plate This angulation prevents overlap of images of two mastoid bones Radiograph for each mastoid is taken separately The Schullers view serves as an alternative view to the Law projection which uses a 15 degree angle of patient's face toward the image receptor and a 15 degree caudal angulation of the CR to achieve the same result, a lateral mastoid air cells viewView and Download PowerPoint Presentations on Steam Inhalation PPT Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPointcom, find free presentations research about Steam Inhalation PPTThe oblique view Xray test scans the mastoid bone from a lateral angle Like a usual Xray test, low radio waves are passed through the ear and lower head portion The waves scan the internal condition of the area and produce an image onto the computer screen You are required to remain still during the process of scanning
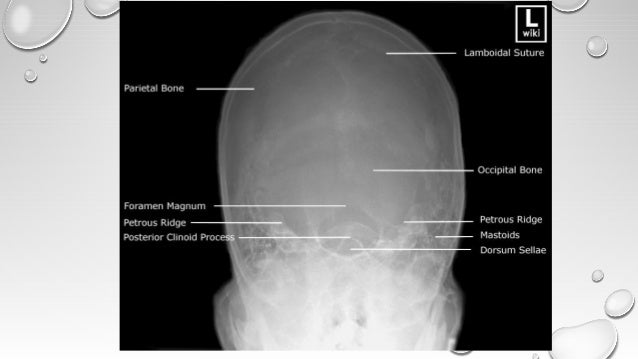



Radiological Imaging In Head And Neck And Relevant Anatomy




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
We have been studying how to make xray examination of the temporal bone, middle ear, and mastoid process as simple and informative as possible What is required of us by the otologic surgeon is a demonstration of the middle ear and ossicles, the epitympanic space, bony bridge, aditus, and the mastoid antrum–Chest XRay special views eg Bucky/Decub –XRay ribs/chest unilateral 3 view –XRay ribs/chest bilateral 4 view 711 –XRay sternum 3 view 710 –XRay entire spine AP/LAT 7 –XRay spine 1 view 740 –XRay neck spine 2 or 3 viewName XR Mastoid bilateral Law and Mayer and Stenver and Towne System Head>Mastoidbilateral Component Views Law Mayer Stenver Towne




A And B X Rays Both Mastoids Law S View Showing Radio Opaque Foreign Download Scientific Diagram
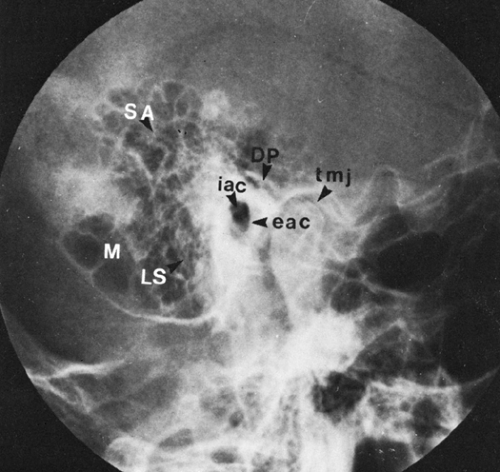



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key
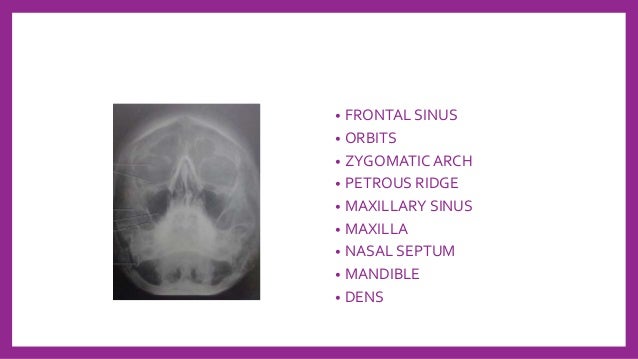



Skull Radiography Techniques And Reporting
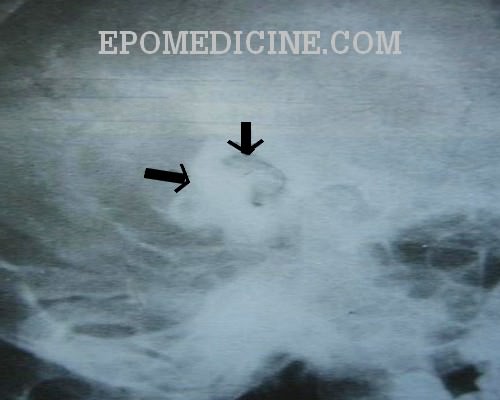



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine
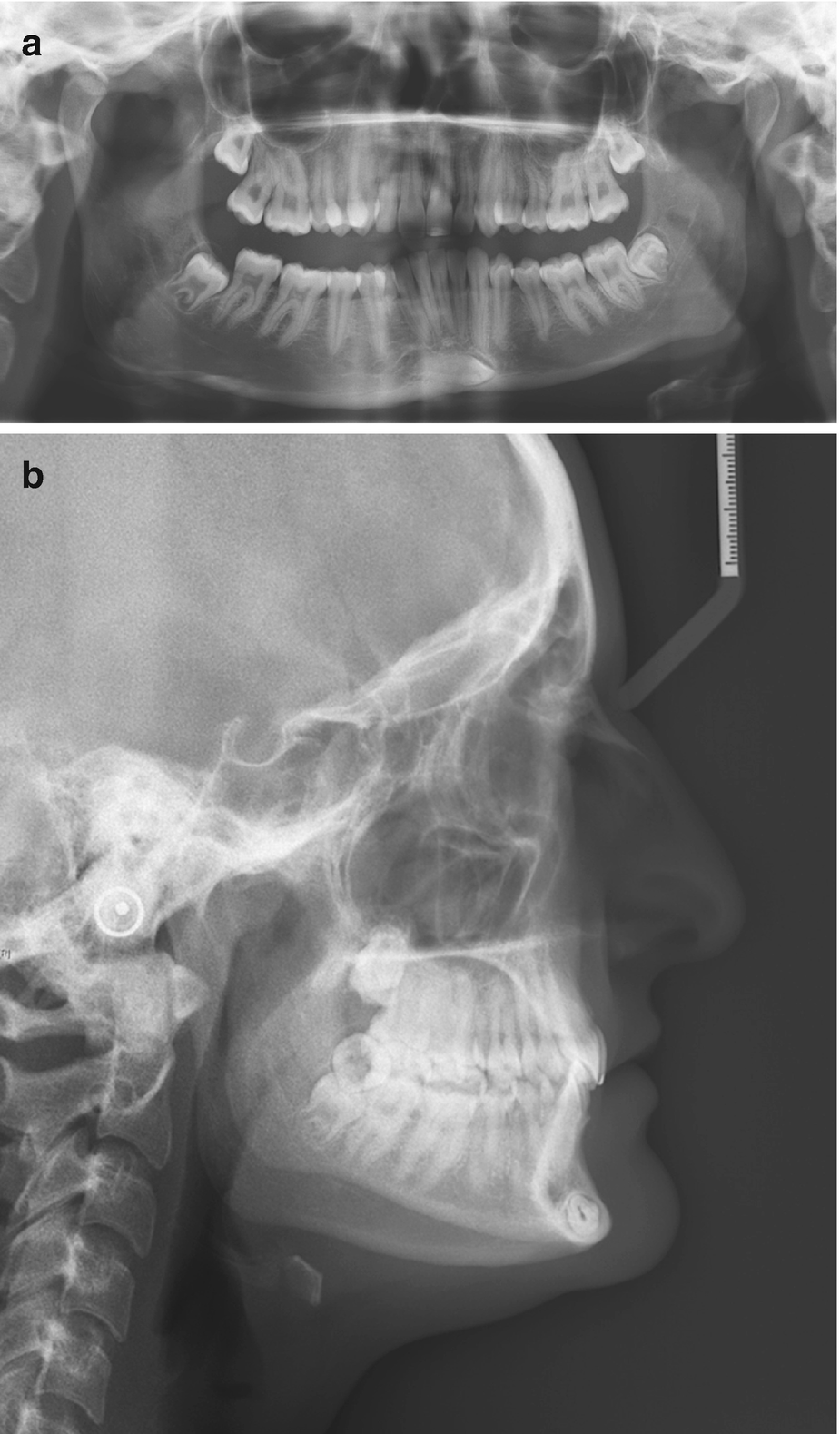



Conventional Radiographic Findings In Tmj Disorders Springerlink




Skull Series Occipitofrontal Projection 0 Cr Clinical Indications




60 Radiographs Labeling Ideas Radiography Radiology Technologist Radiology
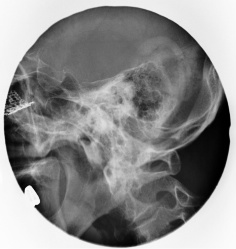



스크랩 Mastoid Law View
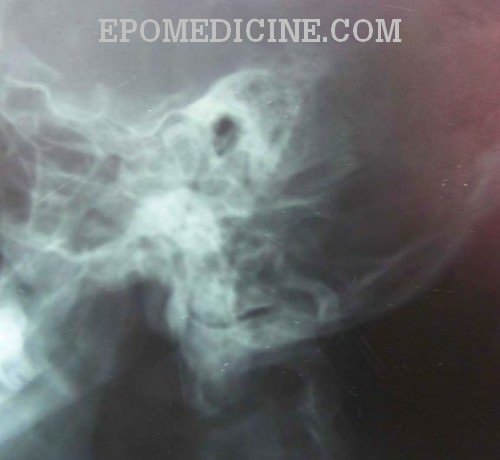



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




Mastoid Stenvers View Youtube



2
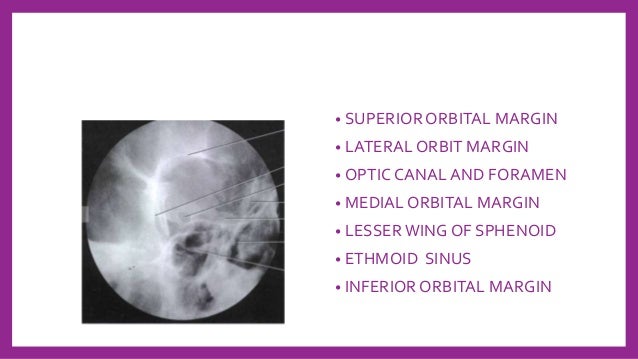



Skull Radiography Techniques And Reporting




View Image
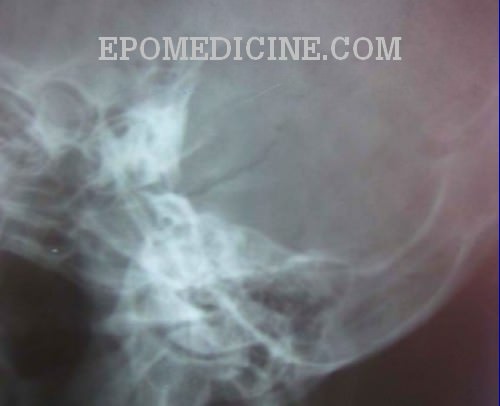



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine
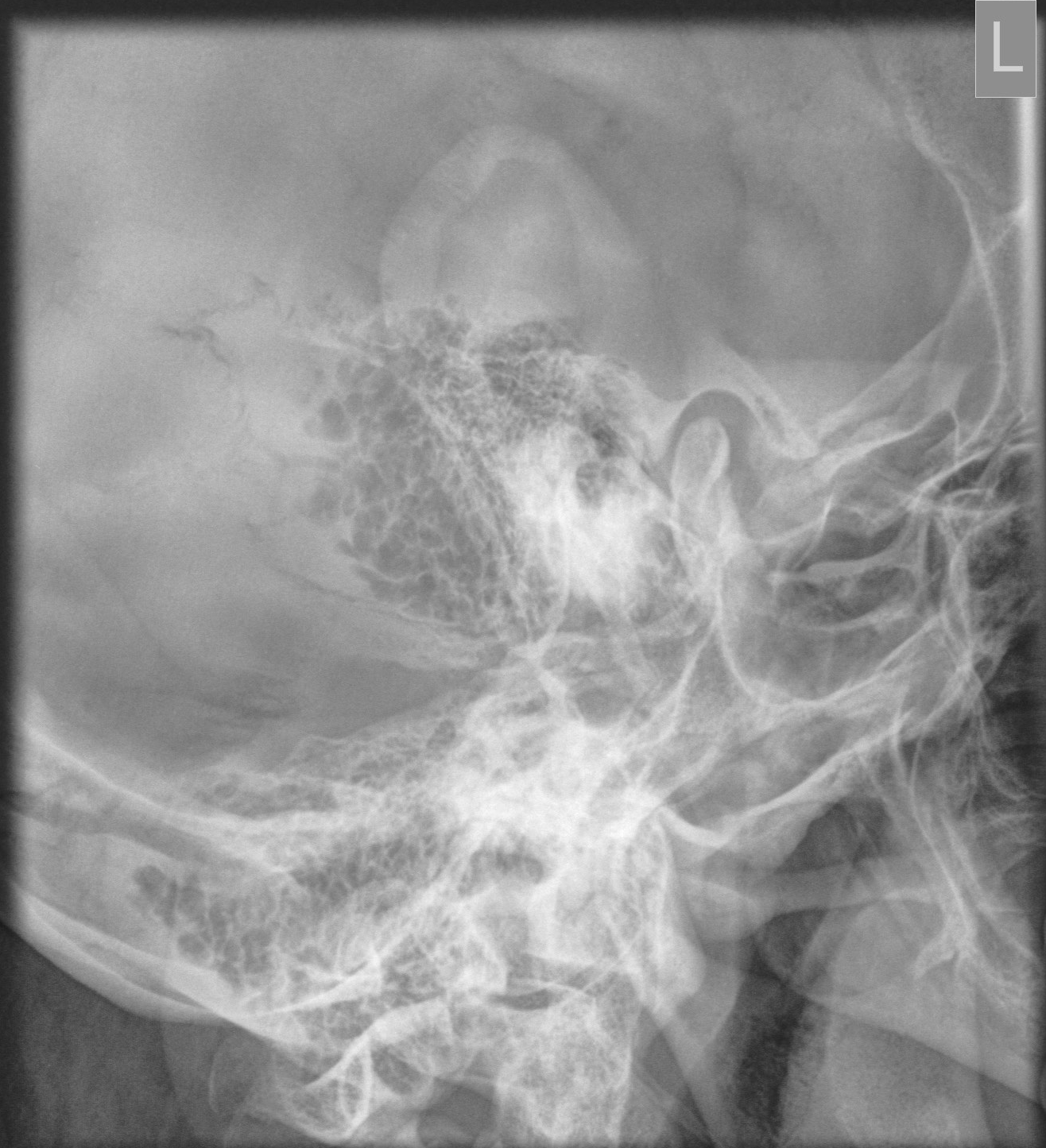



Mastoid Series Normal Image Radiopaedia Org




View Image
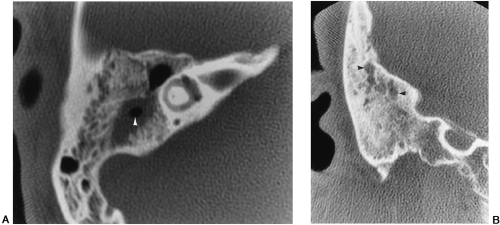



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key



A Comparative Study Of Plain X Ray Mastoids With Hrct Temporal Bone In Patients With Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media Document Gale Academic Onefile



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 1 4471 1724 7 1 Pdf



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 1 4471 1724 7 1 Pdf




Ce4rt X Ray Positioning Of The Mastoid Process For Radiologic Techs




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Neuroradiology Back To The Future Head And Neck Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology
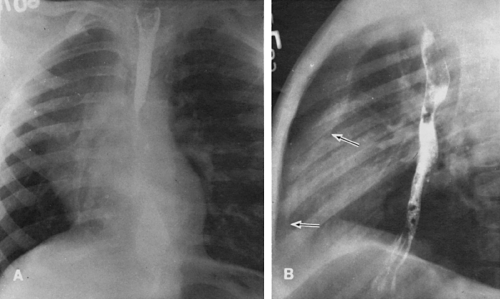



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




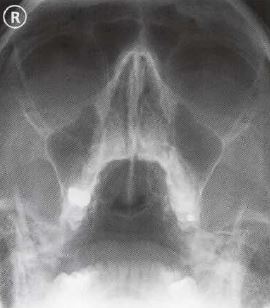
Skull Towne View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Cochlear Implant Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Q Tbn And9gcrvo55xynu9ebeop7emyk3bh41lvbtvulvq 2afm9q Usqp Cau




Pdf Radiographic Imaging Of Mastoid In Chronic Otitis Media Need Or Tradition



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Face And Mandible For X Ray Techs




Mastoids Lat Obl View Anatomy And Physiology Part 23 Youtube




Schuller S View Wikipedia




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




Radiographic Positions Of Mastoids Human Head And Neck Human Anatomy



Diagnostics Free Full Text Deep Learning Based Detection Of Cranio Spinal Differences Between Skeletal Classification Using Cephalometric Radiography Html
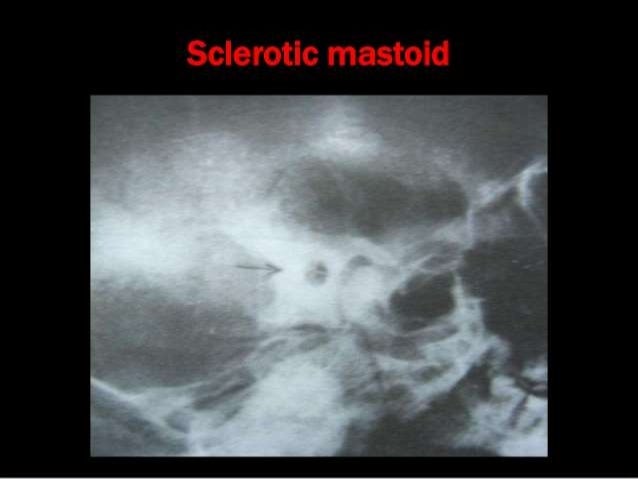



Xrays In Ent Dr Ashly Alexander




Mastoid Series Normal Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
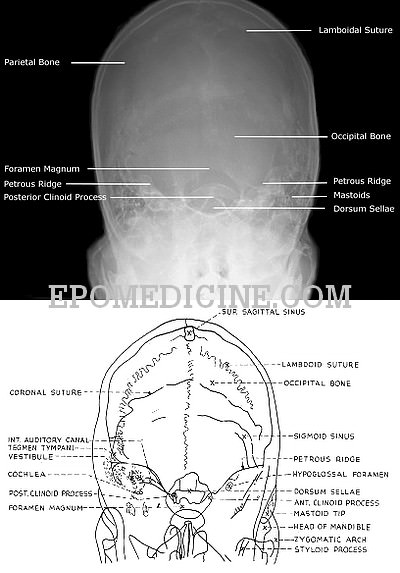



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255
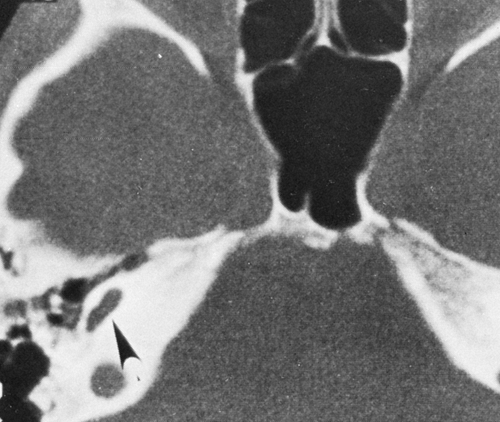



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
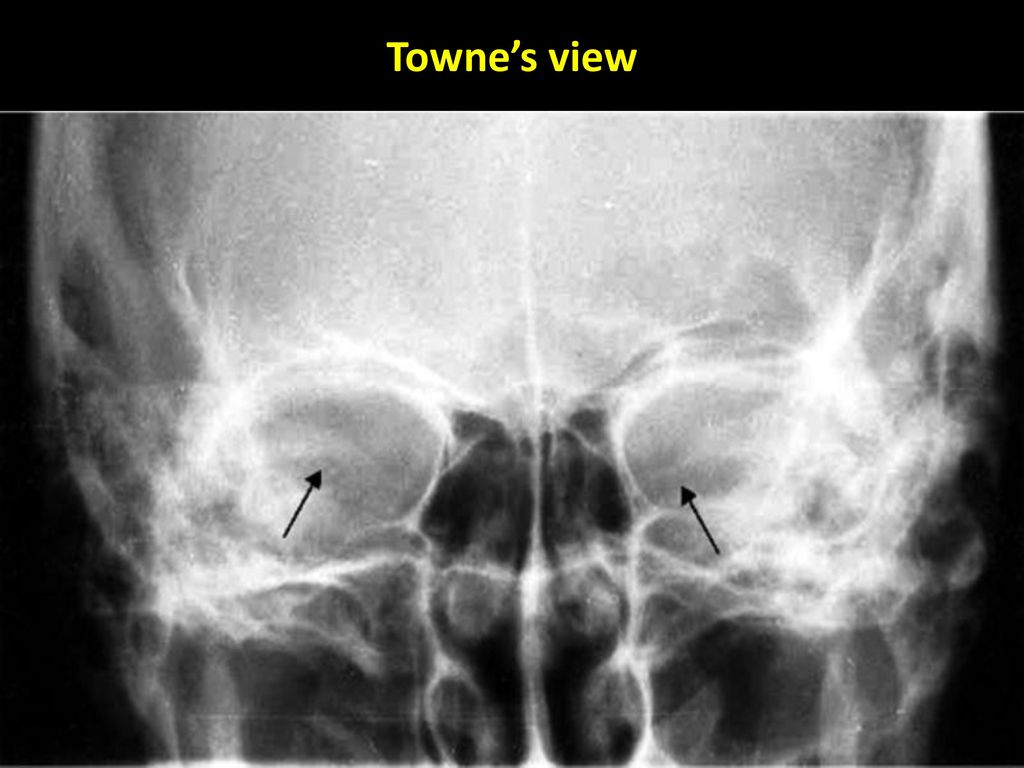



Dr Sujan Chhetri Ms Ent Ppt Video Online Download



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 1 4471 1724 7 1 Pdf




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Mastoid Series Normal Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



100以上 Laws View X Ray Mastoid 2678 Laws View X Ray Mastoid




Mastoids Radiographic Anatomy Medical Radiography Radiology Imaging Medical Knowledge




Stenvers View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Q Tbn And9gctj3zr Hrj2dnckcxuveb Enkdddksnlfto1uq1smrpcw7sbym2 Usqp Cau



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Xrays In Ent Dr Sujan Chhetri Ms Ent




Diseases Of Ear Nose And Throat 6th Edition Pages 451 491 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Petrous Bone




Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Petrous Bone



Www Jemds Com Latest Articles Php At Id 7457




The Modified Stenver S View For Cochlear Implants What Do The Surgeons Want To Know




Laws View X Ray 鬼画像無料



1




Ce4rt X Ray Positioning Of The Mastoid Process For Radiologic Techs




Radiology Quiz Radiopaedia Org



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255




Pps Radiology



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram
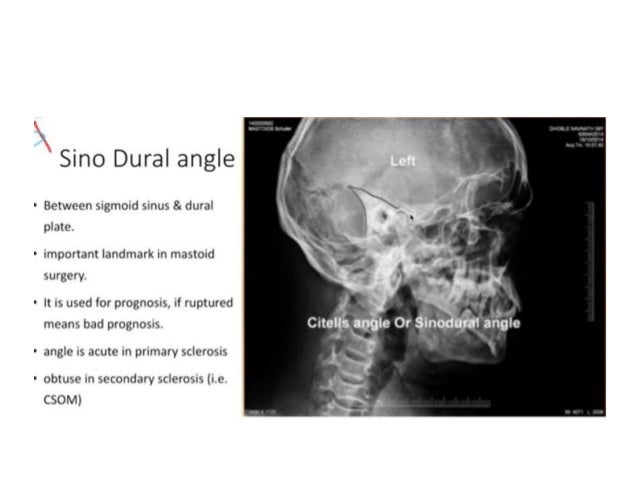



New Microsoft Office Power Point Presentation




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram




Mastoid Ap Axial Towne Methode




X Ray Mastoid Clinics Neetpg Ent Mbbs Youtube
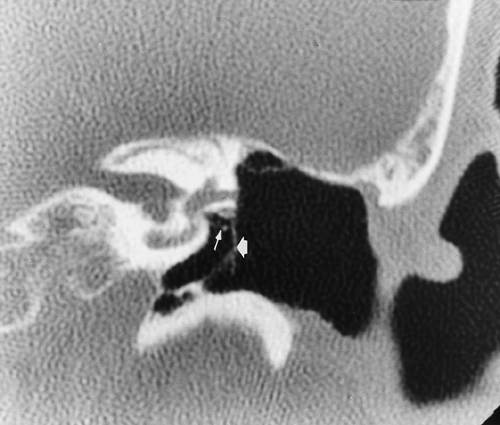



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Mastoids Lat Obl View Anatomy And Physiology Part 23 Youtube



No comments:
Post a Comment